Running Infinispan cluster on OpenShift

Running Infinispan cluster on OpenShift
Did you know that it’s extremely easy to run Infinispan in OpenShift? Infinispan 9.0.0.Alpha4 adds out of the box support for OpenShift (and Kubernetes) discovery!
Our goal
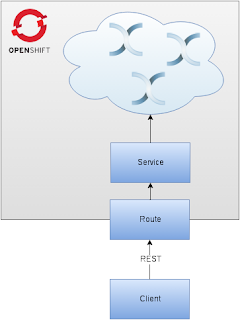
We’d like to build an Infinispan cluster on top of OpenShift and expose a Service for it (you may think about Services as Load Balancers). A Service can be exposed to the outside world using Routes. Finally, we will use REST interface to PUT and GET some data from the cluster.
Accessing the OpenShift cloud
Of course before playing with Infinispan, you will need an OpenShift cluster. There are number of options you can investigate. I will use the simplest path - OpenShift local cluster.
The first step is to download OpenShift Client Tools for your platform. You can find them on OpenShift releases Github page. Once you download and extract the 'oc' binary, make it accessible in your $PATH. I usually copy such things into my '/usr/bin' directory (I’m using Fedora F23).
Once everything is set and done - spin up the cluster:
Note that you have been automatically logged in as 'developer' and your project has been automatically set to 'myproject'.
Spinning an Infinispan cluster
The first step is to create an Infinispan app:
Now you need to modify the Deployment Configuration (use 'oc edit dc/infinispan-server' for this) and tell Infinispan to boot up with Kubernetes' discovery protocol stack by using the proper namespace to look up other nodes (unfortunately this step can not be automated, otherwise a newly created Infinispan node might try to join an existing cluster and this is something you might not want). Here’s my modified Deployment Configuration:
-
(lines 58-60) - Modified Infinispan startup parameters by adding image startup arguments.
-
(lines 88-90) - JGroups Kubernetes Discovery protocol is instrumented by the Downward API to use current project’s namespace.
There is one final step - Kubernetes' PING protocol uses the API to look up other nodes in the Infinispan cluster. By default API access is disabled in OpenShift and needs to be enabled. This can be done by this simple command:
Now we can redeploy the application (to ensure that all changes were applied) and scale it out (to 3 nodes):
Now let’s check if everything looks good - you can do it either through the OpenShift web console or by using 'oc get pods' and 'oc logs' commands:
Accessing the cluster
In order to access the Infinispan cluster from the outside world we need a Route:
The newly created Route needs small changes - we need to change the target port to 8080 (this is the REST service). The 'oc edit route/infinispan-server' command is perfect for it. Below is my updated configuration:
-
(line 17) - Modified to 8080 TCP port
Testing the setup
You can easily see how to access the cluster by describing the Route:
Now let’s try to play with the data:
Cleaning up
Finally, when you are done with experimenting, you can remove everything using 'oc delete' command:
Conclusion
Running Infinispan cluster inside an OpenShift cloud is really simple. Just 3 steps to remember:
-
Create an Infinispan app ('oc new-app')
-
Tell it to use Kubernetes JGroups Stack and in which project look for other cluster members ('oc edit dc/infinispan-server')
-
Allow access to the OpenShift API ('oc policy add-role-to-user')
Happy scaling!
Get it, Use it, Ask us!
We’re hard at work on new features, improvements and fixes, so watch this space for more announcements!Please, download and test the latest release.
The source code is hosted on GitHub. If you need to report a bug or request a new feature, look for a similar one on our GitHub issues tracker. If you don’t find any, create a new issue.
If you have questions, are experiencing a bug or want advice on using Infinispan, you can use GitHub discussions. We will do our best to answer you as soon as we can.
The Infinispan community uses Zulip for real-time communications. Join us using either a web-browser or a dedicated application on the Infinispan chat.