Infinispan 13.0.0.Final

Triskaidekaphobia (/ˌtrɪskaɪˌdɛkəˈfoʊbiə/ TRIS-kye-DEK-ə-FOH-bee-ə, /ˌtrɪskə-/ TRIS-kə-; from Ancient Greek τρεισκαίδεκα (treiskaídeka) 'thirteen', and Ancient Greek φόβος (phóbos) 'fear') is fear or avoidance of the number 13.
However, as you should know by now, the Infinispan team is fearless, and for this reason we are not afraid to proudly announce “Infinispan 13 (Triskaidekaphobia)”. In the grand tradition of our codenames, this one also happens to be the name of a beer (https://www.thebreweryofbrokendreams.com/triskaidekaphobia)

So, don’t be scared and let’s dive into all the new great things that are in this release.
Core
-
Polyglot configuration: XML, JSON and YAML can now be used interchangeably to configure every part of Infinispan. Here is an example of how to configure a cache with eviction and Protobuf encoding:
<distributed-cache> <encoding media-type="application/x-protostream"/> <memory max-size="1.5GB" when-full="REMOVE"/> </distributed-cache>{ "distributed-cache" : { "encoding" : { "media-type" : "application/x-protostream" }, "memory" : { "max-size" : "1.5GB", "when-full" : "REMOVE" } } }distributedCache: encoding: mediaType: "application/x-protostream" memory: maxSize: "1.5GB" whenFull: "REMOVE" -
Max-idle asynchronous touch: max-idle expiration makes reading an entry behave like a write: all owners must update the last access timestamp. With asynchronous touch the reader does not wait for their confirmation, and reading a max-idle entry is as fast as reading any other entry.
-
Metrics for cache size are now optional: calculating the accurate size of a cache is an expensive operation. Starting with this release,
currentNumberOfEntriesandcurrentNumberOfEntriesInMemoryandtotalNumberOfEntrieswill return-1by default. You can re-enable accurate computation of these metrics if you really need them. We will be adding high-performance estimates for these metrics in a future release.
Query
-
Delete by query: Ickle (Infinispan’s query language) now supports
DELETE FROMqueries using all of the supported clauses, both for indexed and non-indexed caches:query.create("DELETE FROM books WHERE page_count > 500").executeStatement();
Persistence
-
The Soft-index file store is now our default persistent file-based cache store. Compared to the old single-file store, it no longer needs to store all keys in memory, plus it supports persistent memory via the awesome Mashona library. Old file stores will be automatically migrated on first use.
-
SQL cache store which maps database tables and queries to Protobuf, greatly simplifying accessing your existing data. For example, you can expose a single table
books:<table-jdbc-store table-name="books"> <schema message-name="books_value" key-message-name="books_key" package="library" embedded-key="true"/> </table-jdbc-store>or use your own queries
<query-jdbc-store> <queries key-columns="isbn"> <select-single>SELECT isbn, title FROM books WHERE isbn = :isbn</select-single> <select-all>SELECT isbn, title FROM books</select-all> <delete>DELETE FROM books WHERE isbn = :key</delete> <delete-all>DELETE FROM books</delete-all> <upsert>INSERT INTO books (isbn, title) VALUES (:key, :value) ON CONFLICT (isbn) DO UPDATE SET title = :value</upsert> <size>SELECT COUNT(*) FROM books</size> </queries> <schema message-name="books_value" key-message-name="books_key" package="library" embedded-key="true"/> </query-jdbc-store>
Server
-
Configuration overlays: you can specify multiple configuration files, in any of the supported formats, and they will be combined to form the final configuration. You can even mix formats:
server.sh -c base.xml -c layer.yml -c custom.json -
Mutable cache configuration: you can now update cache configurations cluster-wide at runtime with the CLI. The following example changes the maximum number of entries of a cache:
alter cache mycache --attribute=memory.max-count --value=10000 -
Thread Pool Consolidation: The prior Infinispan non blocking thread pool has been consolidated with the Netty event loop reducing the number of threads required in the server.
-
REST listeners: It is now possible to listen to cache events over HTTP using Server-Sent Events.
curl --digest -u user:password -N http://127.0.0.1:11222/rest/v2/caches/mycache?action=listen event: cache-entry-created data: data: { data: "_type": "string", data: "_value": "k1" data: } event: cache-entry-modified data: data: { data: "_type": "string", data: "_value": "k1" data: } event: cache-entry-removed data: data: { data: "_type": "string", data: "_value": "k1" data: } -
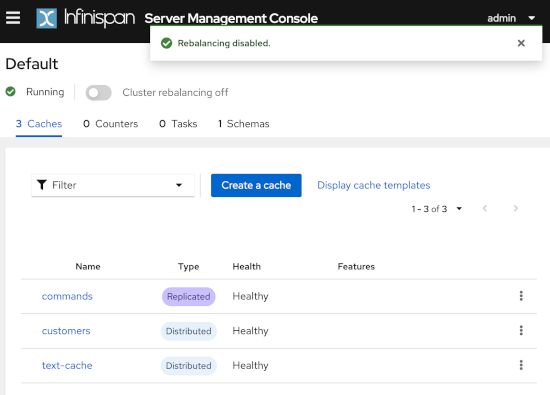
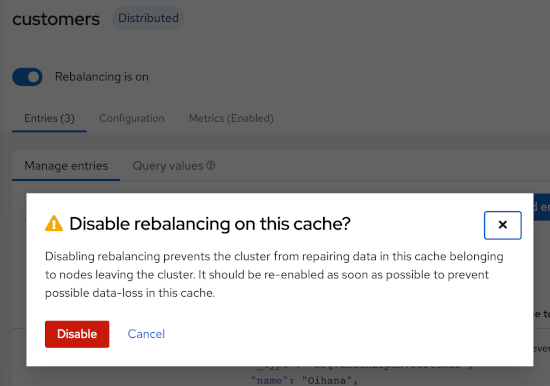
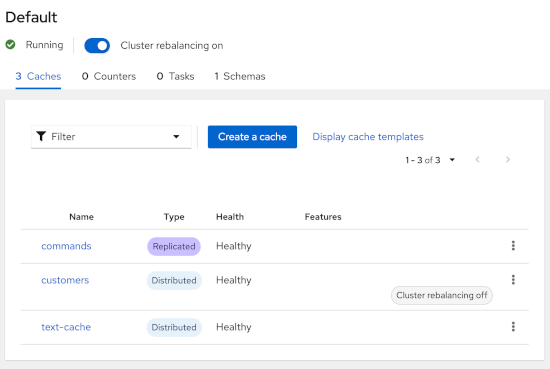
Rebalancing management: control cluster re-balancing from the REST API, CLI, and Console.
-
Simple TLS for clustering: Infinispan Server can automatically enable TLS for the cluster transport simply by specifying a security realm with a keystore/truststore server identity:
<cache-container name="default" statistics="true"> <transport cluster="cluster" server:security-realm="cluster"/> </cache-container> -
Distributed Security Realm: a server security realm which can aggregate multiple sub-realms, trying each one in turn. For example, you can use this to support both certificate and password authentication on the same server.
-
PEM key/trust stores: Support for PEM files for both keys and certificates without the need to convert them to Java keystores first.
-
Full support for TLSv1.3 via native OpenSSL.
Cluster Migration
We’ve done quite a lot of work on the cluster igration operations, making the process smoother from the REST API, CLI, and with our Kubernetes Operator.
-
Manually changing configurations of the cache(s) is no longer necessary
-
New methods in the REST API to control the migration
-
Caches created dynamically are now supported
-
Simplified configuration
Cross-site replication
-
Improve cross-site replication observability
-
The cross-site view (sorted list of site names currently online) and relay-nodes (members who are responsible for relaying messages between sites) are now exposed via CLI/REST/JMX.
-
Detailed metrics exposed per site and per cache (response times, number of messages)
-
Improve some error messages with more details.
Cloud
-
Helm charts: create Infinispan clusters with a Helm chart that lets you specify values for build and deployment configuration. Server configuration is declared using Yaml in .Values. This allows the server configuration to be customized entirely without having to update helm-chart templates locally.
-
Operator: many fixes and improvements:
-
Migrated operator-sdk from v0.18.0 → v1.3.2
-
Migrated packagemanifest → OLM bundle format
-
K8s 1.22 deprecated APIs removed
-
Kubernetes CLI
-
Easily connect a CLI to an operator-managed Infinispan cluster without having to specify connection details:
kubectl infinispan shell -n default mycluster [mycluster-0-37266@mycluster//containers/default]>
Testing
-
An InfinispanContainer which makes it easy to test your applications via the awesome Testcontainers library
try (InfinispanContainer container = new InfinispanContainer()) { container.start(); try (RemoteCacheManager cacheManager = container.getRemoteCacheManager()) { RemoteCache<Object, Object> testCache = cacheManager.administration().getOrCreateCache("test", DefaultTemplate.DIST_SYNC); testCache.put("key", "value"); assertEquals("value", testCache.get("key")); } }
Clustered Counters
-
Strong counters can now expire (experimental). The counter value is reset to its initial value which may be useful to code a cluster-wide rate limiter.
Other
-
Works with JDK 17 (and still works with JDK 8 and JDK 11)
-
Lots of bug fixes
Documentation and tutorials
-
Updated cache configuration docs with tabbed examples with JSON and YAML.
-
Added new guides for indexing and querying caches, Hot Rod clients, and Helm charts.
-
Re-organized Infinispan simple tutorials as part of the ongoing effort to clearly separate remote caches from embedded caches in our content. Infinispan simple tutorials now have their own documentation on our site at: https://infinispan.org/tutorials/simple/simple_tutorials.html
-
Updated documentation for configuring persistent cache stores and JVM memory management, including revisions to improve style, grammar, and provide high-level scanning and readability.
-
Replaced the Integration Guide with a dedicated guide for Spring users as well as a guide for Hibernate caches. We’ve also linked to community projects with Quarkus, Vert.x, Keycloak, Camel, and WildFly. Check out the new Integrations category on the docs home page at: https://infinispan.org/documentation/
Be sure to read through Upgrading Infinispan before getting started with lucky 13.
Get it, Use it, Ask us!
We’re hard at work on new features, improvements and fixes, so watch this space for more announcements!Please, download and test the latest release.
The source code is hosted on GitHub. If you need to report a bug or request a new feature, look for a similar one on our JIRA issues tracker. If you don’t find any, create a new issue.
If you have questions, are experiencing a bug or want advice on using Infinispan, you can use GitHub discussions. We will do our best to answer you as soon as we can.
The Infinispan community uses Zulip for real-time communications. Join us using either a web-browser or a dedicated application on the Infinispan chat.