Infinispan 15.0.0.Final

Don’t you know I’m still standin' better than I ever did? Lookin' like a true survivor, feelin' like a little kid
Those lyrics certainly apply to our newest, and best, release: Infinispan 15, which continues to improve on its mature foundation, and yet packs fun new features, just like a little kid. And in our grand tradition of codenames based on beers, this one is no exception.

JDK requirements
You will need at least JDK 17 in order to use Infinispan 15. Infinispan also supports JDK 21 and the soon-to-be-released JDK 22.
Jakarta EE
Since we’ve completely embraced JDK 17, we now only ship Jakarta EE-compatible modules. If you want to keep on using Java EE, you will have to stay on Infinispan 14, which is still supported.
Redis protocol
Infinispan Server now comes with a Redis protocol (RESP) connector. We implement over 90 commands from Redis OSS, including most data types (strings, sets, sorted sets, lists, hashes, pubsub). Why would you want to use Infinispan instead of Redis ? Just some things:
-
multi-threaded: take advantage of multiple cores without resorting to clustering
-
P2P clustering: all members of a cluster are of the same kind. You don’t need to worry about writing to masters, reading from replicas: it’s all the same! Elastically add/remove nodes at runtime to increase/decrease capacity as required by your workload: Infinispan will rebalance the data to ensure that your redundancy settings are respected.
-
multiple caches with dedicated configuration: divide your data in different namespaces, possibly with different expiration, eviction, persistence rules. And it also works in a cluster, unlike Redis Cluster.
-
cross-site replication: work with 2 or more sites
-
multiple persistence options: store your data on disk, in a database or in another external store. You can even write your own to implement true inline caching instead of side-caching to reduce your overall latency.
-
integration with external identity providers: authenticate/authorize with OAuth2, LDAP, Kerberos, client certificates.
-
full pipeline inbound process handling allows for even greater batched throughput
-
a mature, open-source Kubernetes Operator which supports provisioning, scaling, persistence, and integration with enterprise security.
-
lots more!
-
and everything is available under the ASL 2.0, so you don’t have to worry about features being locked behind restrictive licenses.
The Redis connector is exposed via our single-port: we automatically detect RESP clients on connection!
We even made a video highlighting some cool things!
Vector indexes
Infinispan now supports distributed vector indexes and KNN queries.
They are expressed in Ickle (SQL-like) syntax using the special operator <→. For instance:
Query<Item> query = cache.query("from Item i where i.byteVector <-> [7,6,7]~3");Vector parameters can be passed in different ways. As an entire entity:
query = cache.query("from model.Item i where i.byteVector <-> [:a]~:b");
query.setParameter("a", new byte[]{7, 6, 7});
query.setParameter("b", 3);Or using a placeholder for each cell:
query = cache.query("from model.Item i where i.floatVector <-> [:a,:b,:c]~:d");
query.setParameter("a", 1);
query.setParameter("b", 4.3);
query.setParameter("c", 3.3);
query.setParameter("d", 4);Both float vectors and byte vectors are supported.
Infinispan can be easily integrated into a Python Langchain application as a vector store for semantic search or even in a chain: the picture below shows a QA chain in action.
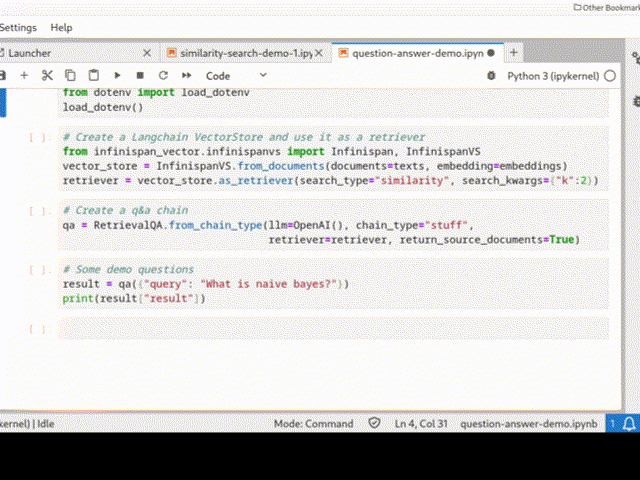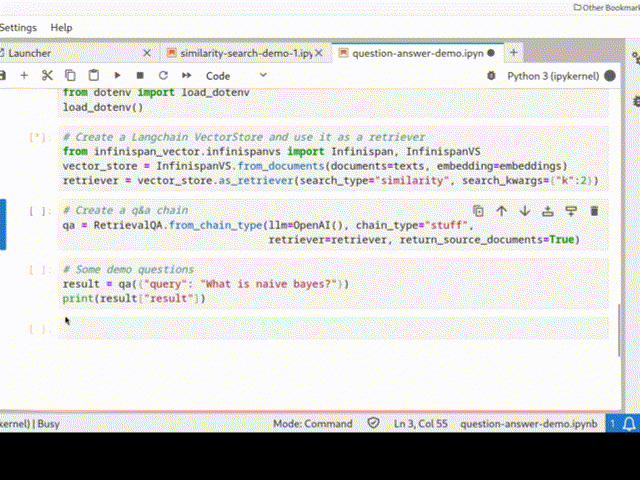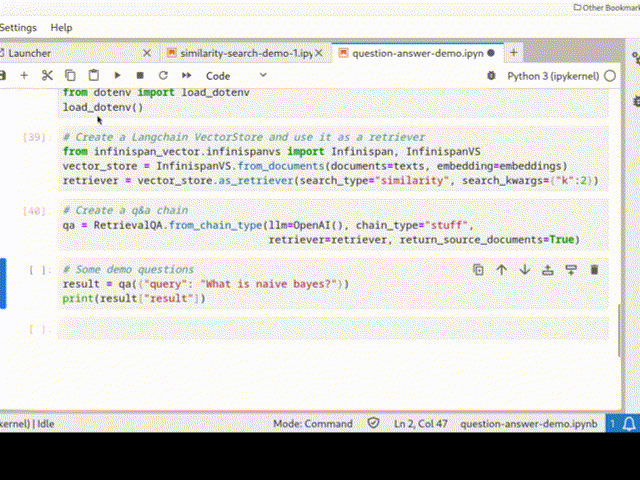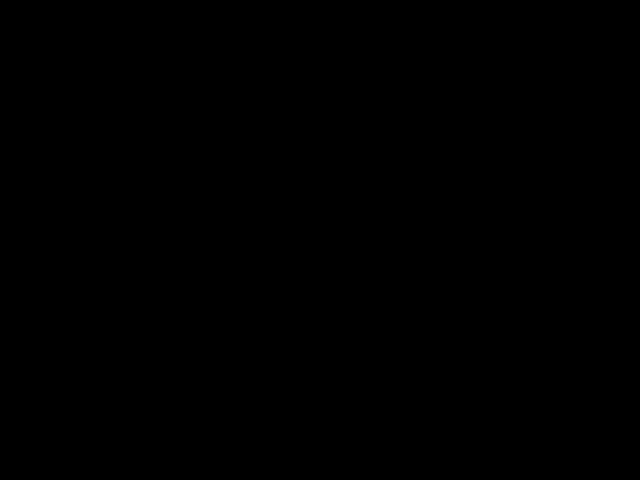
See Infinispan VectorStore and Infinispan Langchain demo for more examples.
Infinispan is also part of Langchain4j, thus the Quarkus Langchain4j quarkiverse extension. It can be used as an embedding store thanks to the support added to vector search.
Query
We finally made it easy to execute queries directly from the cache API, instead of having to go through the Search/QueryFactory combination:
Query<Image> query = cache.query("from play.image where moment between :from and :to order by moment desc");
query.setParameter("from", fromDate);
query.setParameter("to", toDate);The query result object evolved to provide accurate information about the hit count.
QueryResult<Game> result = query.execute();
HitCount hitCount = result.count();
hitCount.value() // returns the value
hitCount.isExact() // returns the accuracyMoreover, hit count accuracy can be configured both globally and for each query execution to improve the performance of the queries.
-
the efficiency of the #list query method has been improved.
-
High-performance indexed count aggregation queries are now supported.
-
More projections kinds have been added:
-
Score
-
Version
-
Star/Identity
and they are now available also using the REST query APIs.
-
-
BigDecimal and BigInteger types are now supported on the ickle queries.
-
index sharding is now configurable.
-
indexing can be now configured in manual mode.
-
index statistics now also contain the faults.
-
the index engine is now called in a non-blocking fashion.
Tracing
The tracing subsystem configuration was greatly improved. Tracing can be configured both globally:
<cache-container name="default">
<tracing collector-endpoint="${infinispan.tracing.collector-endpoint}" security=”true” />
</cache-container>and per-cache:
tracing:
enabled: true
categories:
- "container"
- "cluster"
- "persistence"
- “x-site”Moreover, many more things can be traced: * cluster calls * cross-site calls * persistence operations * security audit operations
All of the aboive, with the only exception of the security tracing, can be enabled / disabled at runtime.
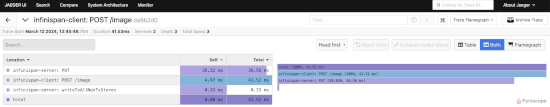
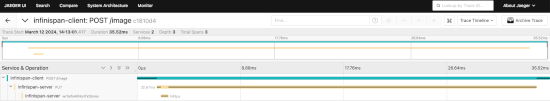
The following is a trace going from client application to the server via Hot Rod, involving a call to a persistent store;.
Console
Core
Many of the core optimizations have been around optimizing intra-cluster communications, especially around previous values that were identified being returned when they are not needed. This ensures Infinispan only sends the cache value around only in the case of put operations, reducing those payloads substantially.
Remove Operations behavior change
Remove operations on a non tx cache will no longer generate intra-cluster traffic if no value is present. Cross sit removes are still always replicated due to not knowing if the other site has the key or not. Stores may load the key to see if it is present to invoke a remove or not, depending on the cache configuration. This also may prevent some listeners from receiving remove notifications, since the operation is not replicated.
Writes on Backup Nodes do not retrieve previous value
Internally write operations would be performed on backup nodes returning the previous value to the primary owner. There is no need for this and as such we have optimized intra cluster communication to no longer return this value.
Converter Listener can ignore old value
Listener converters can override a new method includeOldValue. This allows for a converter to not send an old value along in a change event, reducing payload size of such events. This is useful for events where they only utilize the new value. Link to the source.
An example of a converter that just appends the new value and lifespan as the value for the listener.
@ProtoName("StringAppender")
public static class StringAppender implements CacheEventConverter<Object, String, String> {
@Override
public String convert(Object key, String oldValue, Metadata oldMetadata, String newValue, Metadata newMetadata, EventType eventType) {
return oldValue + (oldMetadata != null ? oldMetadata.lifespan() : "null") + newValue + (newMetadata != null ? newMetadata.lifespan() : "null");
}
/**
* Whether the old value should be returned in the event with the converted value.
*/
@Override
public boolean includeOldValue() {
return false;
}
}Marshalling
Our ProtoStream library, which handles annotation-based generation of Protocol Buffers marshallers, has been updated to finally support the proto3 syntax, including the map type. ProtoStream can now generate marshallers for Java records, as well as introducing a new annotation @Proto which makes life much simpler:
@Proto
@Indexed
public record Book(
@Text String title,
@Keyword(projectable = true, sortable = true, normalizer = "lowercase", indexNullAs = "unnamed", norms = false) String description,
int publicationYear,
Set<Author> authors,
Type bookType,
BigDecimal price
) { }ProtoStream’s programmatic API has also received some love: you can now generate schemas from your code, and you can easily implement hand-written marshallers in case the annotation-based magic doesn’t work for you.
Schema schema = new Schema.Builder("magazine.proto")
.packageName("magazine_sample")
.addMessage("Magazine")
.addField(Type.Scalar.STRING, "name", 1)
.addField(Type.Scalar.INT32, "publicationYear", 2)
.addField(Type.Scalar.INT32, "publicationMonth", 3)
.addRepeatedField(Type.Scalar.STRING, "stories", 4)
.build();
FileDescriptorSource file = FileDescriptorSource.fromString("magazine.proto", schema.toString());By popular demand, we have also undeprecated the use of JBoss Marshalling, although we still highly recommend ProtoBuf for interoperability and performance.
Memcached protocol
We upgraded our memcached connector to support the binary protocol as well as supporting authentication and encryption for both the text and binary variants. Because of this, the connector is also exposed via our single-port, with protocol auto-detection! While we do not yet support the Memcached meta commands, text-based authentication can be performed by sending a fake set` command with any key:
set <key> <flags> <exptime> <bytes>\r\n
username password\r\nServer
Server security has been expanded with the new aggregate-realm type, which allows you to combine different realm types for authentication and authorization. For example, you could use client certificates for authentication and an LDAP server to perform authorization:
<server xmlns="urn:infinispan:server:15.0">
<security>
<security-realms>
<security-realm name="default" default-realm="aggregate">
<server-identities>
<ssl>
<keystore path="server.pfx" password="secret" alias="server"/>
<truststore path="trust.pfx" password="secret"/>
</ssl>
</server-identities>
<properties-realm groups-attribute="Roles">
<user-properties path="users.properties" relative-to="infinispan.server.config.path"/>
<group-properties path="groups.properties" relative-to="infinispan.server.config.path"/>
</properties-realm>
<truststore-realm/>
<aggregate-realm authentication-realm="trust" authorization-realms="properties">
<name-rewriter>
<common-name-principal-transformer/>
</name-rewriter>
</aggregate-realm>
</security-realm>
</security-realms>
</security>
</server>Persistence
Along with the sub changes below we also have optimized persistent entries that do not have expiration or other custom metadata, reducing marshalled byte size by approximately 40 bytes per entry.
Soft-Index File Store
The underlying index for the Soft Index File Store has been completely revamped to no longer utilize a different set of “segments” for its index. Instead it splits its index into a number equal to the caches configured segments (ie. cache → clustering → hash → number of segments). The “index segments” configuration is now deprecated and ignored.
This change allows for more efficient segment based operations. Iteration within a subset of segments now only needs to read a single file instead of multiple. Cache rebalance with DIST is now orders of magnitude faster as it just drops a single index Key lookup is also now slightly faster (on average 4 less hash comparisons)
Index files now also utilize a portion of the open files limit to prevent possibility of file descriptor exhaustion. By default the index will use up to 10% of the file limit to keep files open, closing as needed.
Passivation
Passivation has been changed to be less chatty. Originally passivation required contents to only be in memory or in the store. This has been found to generate too many write operations to the underlying store. Instead now it is permitted that a value be stale in the store when it is present in memory. This prevents many remove operations from being generated. Upon shutdown or if the entry is evicted from memory only then will the store be updated with the proper value.
With a clean shutdown there will be no data inconsistency with a restart. It should be noted that if the node crashes without proper shutdown the cache may have a stale value (new behavior) instead of no value (previous behavior) for values that were in memory.
Operator
-
Configure Readiness, Liveness and Startup probe values
-
Expose JMX endpoint
-
Configuration of StatefulSet PriorityClass
-
Allow users to define credential-store entries
-
ConfigListener configure CPU and Memory resources
-
Make cross-site failure detection configurable
-
Use TLSv1.3 as default for Xsite
-
Xsite GossipRouter improvements
-
Allow setting the CPU and Memory resources
-
Added and enabled heartbeats by default
-
Disabled suspect events by default
-
TLS client authentication by default
-
Increase the probe timeout
Helm charts
-
Add ability to define custom environment variables
-
Add ability to set tolerations
-
Add support for node affinity and node selectors
-
Allow the user to specify container securityContext
-
Allow TLS configuration on endpoints
-
Allow TLS configuration on JGroups transport
GraalVM
In addition to our various Quarkus integrations, Infinispan now provides the infinispan-client-hotrod-graalvm and infinispan-core-graalvm modules. These modules enable you to build native Hot Rod clients and Embedded Infinispan applications natively with GraalVM, allowing integration with other frameworks such as Spring Broot.
Security Manager
We have completely removed support for the Java Security Manager, since it has been deprecated for removal in the JDK. It was designed mostly for sandboxing Java applets, but it was somehow (wrongly) co-opted as a way to implement similar functionality for normal Java applications. It was slow and cumbersome, and we’re glad to see it go. The removal of SecurityManager support from Infinispan does not affect its authentication and authorization capabilities.
Integrations
-
Our second-level cache component now supports Hibernate ORM 6.4
-
We have dropped CDI support from our JCache provider since the specification has not been updated for Jakarta EE
Removals
Sadly, a couple of items have been removed, as we did not see much use in the wild: scattered caches and the cloud-events integration module. May they rest in peace.
Documentation
Many improvements, updates and fixes.
Release notes
You can look at the release notes to see what has changed since our latest CR.
Get them from our download page.
Get it, Use it, Ask us!
We’re hard at work on new features, improvements and fixes, so watch this space for more announcements!Please, download and test the latest release.
The source code is hosted on GitHub. If you need to report a bug or request a new feature, look for a similar one on our JIRA issues tracker. If you don’t find any, create a new issue.
If you have questions, are experiencing a bug or want advice on using Infinispan, you can use GitHub discussions. We will do our best to answer you as soon as we can.
The Infinispan community uses Zulip for real-time communications. Join us using either a web-browser or a dedicated application on the Infinispan chat.