Monday, 23 December 2019
Infinispan 10.1.0.Final
Hi there,
we finish 2019 in style with the Final release of Infinispan 10.1, codenamed "Turia".
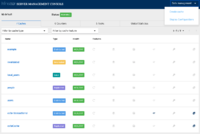
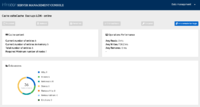
Server console
The highlight of this release is the new server console which is now based on Patterfly 4 and React.js. We will soon have a blog post detailing the work that has been done and our future plans. In the meantime, here are a few screenshots:
Security
Many changes related to security have happened since 10.0:
-
Native SSL/TLS provided by WildFly OpenSSL. The server only ships with native libraries for Linux x86_64, but you can download natives for other platforms and architectures
-
Improved usability of the Hot Rod client configuration with better defaults
-
Full support for authorization for admin operations via the RESTful endpoint
-
Console authentication support
-
Kerberos authentication for both Hot Rod (GSSAPI, GS2) and HTTP/Rest (SPNEGO)
-
Improved LDAP realm configuration with connection tuning and attribute references
-
Rewritten client/server security documentation including examples on how to create certificate chains, connecting to various LDAP directories and KeyCloak, etc.
Server
-
A command-line switch to specify an alternate logging configuration file
-
Query and indexing operations/stats are now exposed over the RESTful API
-
Tasks and Scripting support
-
Support for binding the endpoints to 0.0.0.0 / ::0 (aka INADDR_ANY)
Non-blocking
More work has landed on the quest to completely remove blocking calls from our internals. The following have been made non-blocking:
-
State transfer
-
The size operation
-
Cache stream ops with primitive types
Additionally caches now have a reactive Publisher which is intended as a fully non-blocking approach to distributed operations.
Monitoring
-
The introduction of histogram and timer metrics.
-
The
/metricsendpoint now includesbaseandvendormicroprofile metrics
Removals and deprecations
-
The old RESTful API (v1) has been partially reinstated until 11.0. Bulk ops are disabled.
-
The Infinispan Lucene Directory has been deprecated.
-
The memcached protocol server has been deprecated. If you were relying on this, come and talk to us about working on a binary protocol implementation.
Bug fixes, clean-ups and documentation
Over 160 issues fixed including a lot of documentation updates. See the full list of changes and fixes
Get it, Use it, Ask us!
Please download, report bugs, chat with us, ask questions on StackOverflow.
Tags: release
Monday, 09 December 2019
Infinispan 10.1.0.CR1
Dear Infinispan community,
as we are closing in on 10.1, we have been working on a lot of polishing and bugfixing.
Server
-
The new console has received a lot of improvements,
-
A new welcome page
-
A command-line switch to specify an alternate logging configuration file
Removals and deprecations
-
The old RESTful API (v1) has been removed
-
The Infinispan Lucene Directory has been deprecated.
-
The memcached protocol server has been deprecated. If you were relying on this, come and talk to us about working on a binary protocol implementation.
Bug fixes, clean-ups and documentation
Over 40 issues fixed including a lot of documentation updates. See the full list of changes and fixes
Get it, Use it, Ask us!
Please download, report bugs, chat with us, ask questions on StackOverflow.
Infinispan 10.1.0.Final is scheduled for December the 20th.
Tags: release candidate release
Monday, 25 November 2019
Infinispan Operator 1.0.1
Dear Infinispan community,
we know you are happy with the new shining 10.0.0 Infinispan release, but if you are among those who are missing a new operator version for safely running your Infinispan Chupachabra in the clound, this post is for you!
Versioning and channels
This is our first blog post about 1.0.x operator series (yeah, sorry 1.0.0 we forgot about you) and as you can notice there’s no Alpha, Beta or CR label at the end of the release tag. This is because OperatorHub and Openshift Catalog only allow numerical version like Maj.Min.Mic and instead of labels we now use the channel to indicate the stability of a release. We have 2 live channels at the moment for the Infinispan operator: stable and dev-preview. Current stable is 0.3.2 which is for the 9.x Infinispan cluster and current dev-preview is 1.0.1 which works with 10.x clusters.
New features
-
New Infinispan image configuration: we cleaned up the image configuration process: instead of rely on a large set of env variables, now the operator configures the Infinispan image via a single .yaml file.
-
Container configurability: CR .yaml file lets you configure memory and CPU (and also extras Java opts) assigned to the container;
-
Encryption: TLS can be setup providing TLS certificates or using platform service as the Openshift seriving certs service (TLS will be on by default in the next release);
-
We now have some good docs: https://infinispan.org/infinispan-operator/master/operator.html;
-
Project README has been also improved: https://github.com/infinispan/infinispan-operator/blob/1.0.1/README.md;
Get it
The Infinispan Operator 1.0.1 works on Kind/Kubernetes 1.16 (CI) and Openshift 3.11, 4.x (developed on). You can install it:
-
manually, follow the README;
-
with OLM on Kubernetes, https://operatorhub.io/operator/infinispan/dev-preview/infinispan-operator.v1.0.0
-
with OLM from the Openshift Operator Catalog
And remember: it’s a dev-preview release, you can have a lot of fun with it!
Contribute
As usual source code is open at: https://github.com/infinispan/infinispan-operator. You can see what’s going on, comment the code or the new pull requests, ask for new features and also develop them!
Thanks for following us, Infinispan
Tags: dev-preview release
Monday, 18 November 2019
Infinispan 10.1.0.Beta1
Dear Infinispan community,
Quick on the heels of Infinispan 10.0 here comes the first Beta or 10.1.
Server
This release closes the gap between the legacy server and the new server we introduced in 10.0. In particular:
-
The reworked console (which will be described in detail in an upcoming series of blog posts)
-
Kerberos authentication for both Hot Rod (GSSAPI, GS2) and HTTP/Rest (SPNEGO)
-
Query and indexing operations/stats are now exposed over the RESTful API
-
Tasks and Scripting support
Non-blocking
More work has landed on the quest to completely remove blocking calls from our internals. The following have been made non-blocking:
-
the size operation
-
cache stream ops with primitive types
Additionally caches now have a reactive Publisher which is intended as a fully non-blocking approach to distributed operations.
Bug fixes, clean-ups and documentation
Over 40 bug fixes. See the full list of changes and fixes
Get it, Use it, Ask us!
Please download, report bugs, chat with us, ask questions on StackOverflow.
Infinispan 10.1.0.CR1 is scheduled for December the 7th.
Tags: beta release
Friday, 01 November 2019
Infinispan 10.0.1.Final
We are pleased to announce the availability of Infinispan 10.0.1.Final, which contains several bug fixes.
The release notes can be found here.
As usual you can ask questions on the forum, StackOverflow and interactively on our Zulip Chat. Please report any bugs you find on our Issue Tracker
Tags: final release
Monday, 28 October 2019
Infinispan 10.0.0.Final
Dear Infinispan community,
We are very pleased to announce the release of Infinispan 10.0 codenamed “Chupacabra”! We have been busy making many changes over the last months.
Server
Infinispan 10 features a brand new server, replacing the WildFly-based server we’ve had since 5.3 with a smaller, leaner implementation. Here are the highlights:
-
Reduced disk (50MB vs 170MB) and memory footprint (18MB vs 40MB at boot)
-
Simpler to configure, since it shares the configuration schema with embedded with server-specific extensions
-
Single-port design: the Hot Rod, REST and management endpoint are now served through a single port (11222) with automatic protocol detection between HTTP/1.1, HTTP/2 and Hot Rod. The memcached endpoint is handled separately since we don’t implement the binary protocol yet.
-
New CLI with data manipulation operations
-
New REST-based API for administration
-
Security implemented using WildFly Elytron:
-
Hot Rod authentication support for PLAIN, DIGEST-MD5, SCRAM, EXTERNAL, OAUTHBEARER
-
HTTP authentication support for BASIC, DIGEST, CLIENT_CERT and TOKEN
-
Properties, Certificate Store and LDAP realms
-
Integration with KeyCloak
-
Caches/counters are created and managed dynamically through Hot Rod / REST
Because of the amount of restructuring, the web-based Console is not yet available in this release. We are working on it and it will be included in 10.1.
REST Endpoint
A new API (v2) was introduced and users are encouraged to migrate their applications from the old API.
The v2 API offers a completely redesigned endpoint, including dozens of new operations. Besides allowing to manage caches, it also covers cache containers, counters, cross-site replication, servers and clusters.
Apart from the new API, the REST server is now fully non-blocking and also has better performance than 9.4.x. It also fully supports authorization.
Marshalling
The internal marshalling capabilities of Infinispan have undergone a significant refactoring in 10.0. The marshalling of internal Infinispan objects and user objects are now truly isolated. This means that it’s now possible to configure Marshaller implementations in embedded mode or on the server, without having to handle the marshalling of Infinispan internal classes. Consequently, it’s possible to easily change the marshaller implementation user for user types, in a similar manner to how users of the HotRod client are accustomed.
As a consequence of the above changes, the default marshaller used for marshalling user types is no longer based upon JBoss Marshalling. Instead we now utilise the ProtoStream library to store user types in the language agnostic Protocol Buffers format. The ProtoStream library provides several advantages over jboss-marshalling, most notably it does not make use of reflection and so is more suitable for use in AOT environments such as Quarkus.
Persistence
The persistence SPI has had some much needed TLC, with several deprecations and additions. The aim of this work was to ensure that internal Infinispan classes were no longer leaking into the SPI, in order to ensure that custom store implementations only have to be concerned with their data, not internal Infinispan objects.
Stores by default are now segmented when the segmented attribute is not set. A segmented store allows for greater iteration performance and less memory usage. This is useful for things such as state transfer and other operations that require an entire view of the cache (iteration, size, mass indexer distributed streams etc). All of our provided stores now provided being segmented; these include file store, soft index file store, rocks db, jdbc and remote stores.
Container Image
To accommodate our brand new server, Infinispan 10.0 also introduces a completely new container image which is much smaller than the old one (366MB vs 684MB) and supports the following features:
-
Red Hat’s Minimal Universal Base Image based
-
Java 11
-
Simple yaml configuration
-
Authentication (Enabled by default)
-
Encryption
-
Logging
-
XSite support
The new image can be pulled from any of the following repositories:
Metrics and Logging
Infinispan has adopted the MicroProfile Metrics ver. 2.0.2 specification and uses the SmallRye Metrics implementation. MicroProfile Metrics allows applications to gather various metrics and statistics that provide insights into what is happening inside an Infinispan cluster.
The current offering includes both cache container and cache level Gauge type metrics. Histograms and Timers will arrive in the next release of the 10.x stream.
The metrics can be read remotely at the well-known /metrics REST endpoint and use JSON format or optionally the OpenMetrics format, so that they can be processed, stored, visualized and analyzed by compatible tools such as Prometheus.
But rest assured, the existing JMX support for metrics has not been superseded by REST. JMX is still alive and kicking and we plan to continue developing it and have it available on all runtimes that support it (Quarkus being the notable exception).
Logging categories for the major subsystems have been introduced (CLUSTER, CONTAINER, PERSISTENCE, SERVER, etc) so that it easier to understand what they refer to. The server also comes with a JSON logger for easy integration with tools such as Fluentd or the ELK stack.
Quarkus
Infinispan is an official extension in Quarkus! If you wish to find out more about Quarkus you can find it at https://quarkus.io/.
We have a very featureful client extension allowing your Quarkus apps to connect to a remote server with lots of the features you are used to: querying, authentication, encryption, counter, dependency injection and others. We recently added support for protostream based annotation marshalling. If you are curious you can find the code at https://github.com/quarkusio/quarkus/tree/master/extensions/infinispan-client.
The Infinispan embedded extension was also just added, but has limited functionality due to its infancy. Although it will allow you to run an embedded clustered cache in a native executable. If you are curious you can find the code at https://github.com/quarkusio/quarkus/tree/master/extensions/infinispan-embedded.
The Infinispan team has also started adding a standalone project to have a Quarkus based Infinispan Server using Infinispan 10 and newer. This is still a work in progress, but the new repository can be found at https://github.com/infinispan/infinispan-quarkus-server.
Quarkus has a different release cycle than Infinispan, so watch out for more improvements over the following weeks !
Cross-Site Replication
Async mode cross-site replication received 3 major improvements: Concurrent requests (i.e. write on different keys for example) will be handled simultaneously instead of sequentially. Asynchronous mode is now able to detect disconnections between sites and bring the site offline based on <take-offline> configuration (ISPN-10180) Tracks and exposes some metrics for asynchronous requests (ISPN-9457)
Internals
Dependency Injection
Infinispan’s internal dependency-injection has been completely rewritten so that factories, components and dependencies are discovered and resolved at compile time instead of using runtime reflection. This, together with the marshalling changes and recent JGroups changes, paves the way for usage and native compilation with Quarkus.
Non-blocking
Several internal subsystems have been rewritten to be non-blocking, meaning that they will not hold-on to threads while waiting for I/O:
-
Non-blocking Hot Rod authentication (ISPN-9841)
-
Non-blocking REST endpoint (ISPN-10210)
-
Update internal remote listener code to support non blocking (ISPN-9716)
-
Update internal embedded listeners to be non blocking (ISPN-9715)
-
Passivation throughput is increased as well as these operations are done asynchronously.
-
In addition cache stores have been made non blocking for the cases of loading an entry and storing into the data container as well write skew checks. With this we should be at a point where we can start consolidating thread pools, so keep a look-out in the upcoming releases.
-
Distributed Streams utilizing a terminal operator that returns a single value use non blocking communication methods (ISPN-9813)
Off Heap Storage Improvements
Off Heap has added a few improvements to increase performance and reduce memory usage.
-
Iteration imrpovements (ISPN-10574)
-
Removes the need for the address count configuration option
-
Dynamically resize underlying bucket
-
Reorder bucket iteration to more CPU friendly, less lock acquisiations as well
-
-
StampedLock instead of ReadWriteLock (ISPN-10681)
Expiration Improvements
Cluster Expiration has been improved to only expire entries on the primary node to reduce the amount of concurrent expirations from multiple nodes in the cluster. Also the amount of concurrent expirations on a single node has been improved for better handling.
Additionally, expirations are not replicated cross site to reduce chattiness on the cross site link. Also to note that lifespan works fine without this and max-idle expiration does not work properly with cross site. So in this case the messages were providing no benefit.
API
We now have a proper sizeAsync method on the Cache interface. This is both for remote and embedded APIs. This method should be preferred over the current size due to not blocking the invoking thread as well as being able to retrieve the size as a long instead of a int.
Configuration
It is now possible to configure JGroups stacks directly from the Infinispan configuration file. We use this ability to also allow easily creating multiple stacks (for easy cross-site configuration). The distribution comes with several pre-built JGroups stacks for cloud environments which you can quickly adapt for your configuration. Additionally you can extend existing JGroups configurations replacing individual protocols. This makes it easy, for example, to use a different discovery without worrying about all the other protocols.
Documentation
Infinispan community documentation has been going through some big changes over the past year. The Infinispan 10 release marks the first major step towards adopting a modular structure that supports flexible content for specific use cases. On top of that we’ve also been putting lots of effort into transforming our documentation set to adhere to the principles of minimalism that put focus on user goals and delivering leaner, more concise content.
Our 10.0 release also incorporates work to organize content into three main types: task, concept, and reference. Mapping content to information types makes it easier to write and maintain content by removing worries about style, scope, and other complexities. Writers can separate documentation into logical units of information that can stand alone and then assemble topics into tutorials, how-to articles, explanations, and reference material.
You might also notice some changes to the documentation section of our site and updates to the index page for Infinispan 10 docs. Hopefully the new layout makes it easier to navigate and find the information you’re looking for.
We hope you find the improvements to the documentation helpful. As always, we’re keen to get your feedback and would appreciate. And if you feel like getting involved, see the Contributor’s Guide and start writing Infinispan docs today!
Experimental features
Reactive API
First steps to a new Reactive API. This is still a work in progress and the API will see major changes. We plan on making this API final and default in Infinispan 11. The new API includes a new API module and a new KeyValueStore Hot Rod client where search, continuous search and Key Value store methods are included
Removal/deprecations
A new major release is also an opportunity to do some house-cleaning.
Deprecations
-
Deprecate GridFileSystem and org.infinispan.io stream implementations (ISPN-10298)
-
Deprecated Total Order transaction mode (ISPN-10259)
-
Deprecated Externalizer, AdvancedExternalizer and @SerializeWith (ISPN-10280)
Removals
-
AtomicMap implementations (ISPN-10230)
-
Deprecated org.infinispan.io classes (ISPN-10297)
-
org.infinispan.tools.ConfigurationConverter (ISPN-10231)
-
Compatibility mode (ISPN-10370)
-
AtomicObjectFactory (ISPN-10414)
-
C3P0 and Hikari Connection Pools (ISPN-8087)
-
Delta and DeltaAware interfaces (ISPN-8071)
-
HotRod 1.x support (ISPN-9169)
-
Tree module (ISPN-10054)
-
Distributed Executor (ISPN-9784)
Get it, Use it, Ask us!
Please download, report bugs, chat with us, ask questions on StackOverflow.
Tags: final release
Monday, 15 July 2019
Infinispan 10.0.0.Beta4
Dear Infinispan users,
it has been a while since our last release and quite a few things have been cooking in the Infinispan furnace. Bear in mind that the list below should just serve as a summary and that dedicated blogs, documentation and examples will appear in the near future.
Server
Since 5.3, our server has been built on top of WildFly (JBoss AS7 at the time). WildFly gave us a very solid base, including integration with a lot of useful components (security, datasources, management etc) but it also forced us to maintain a large amount of integration code. We have therefore decided to start from a much leaner base to build the new server which, internally we’ve been calling ServerNG, but which we’re now releasing as "Infinispan Server". The old WildFly-based server is still available, but it should be considered "legacy" and will no longer receive any feature enhancements.
The new server deserves its own dedicated post, but its main features are:
-
smaller size (36MB vs 130MB)
-
smaller memory footprint (20MB heap usage at boot vs 40MB)
-
single-port: the Hot Rod, REST and management endpoint are now served through a single-port (11222) with automatic protocol detection between HTTP/1.1, HTTP/2 and Hot Rod. The memcached endpoint is handled separately since we don’t implement the binary protocol yet.
-
security implemented using WildFly Elytron currently supporting PLAIN, DIGEST-MD5, SCRAM, EXTERNAL mechs for Hot Rod, BASIC, DIGEST, CLIENT_CERT for REST/HTTP (OAuth/JWT/GS2/GSSAPI/SPNEGO will be coming in the next releases)
-
the server configuration extends the embedded configuration scheme
-
caches/counters are created and managed dynamically through Hot Rod / REST.
Marshalling
Infinispan’s marshalling has received a significant overhaul and it is now split into three distinct marshallers: Internal, Persistence and User (ISPN-7409 ISPN-9621) The Persistence marshaller is now based on ProtoBuf allowing for long-term compatibility of data stored in memory and in cache stores. The Store Migrator has been updated to allow migration from Infinispan 8.x/9.x cache stores to the new format (ISPN-10276)
Core changes
Infinispan’s internal dependency-injection has been completely rewritten so that factories, components and dependencies are discovered and resolved at compile time instead of using runtime reflection. This, together with the marshalling changes and recent JGroups changes, paves the way for usage and native compilation with Quarkus.
REST
The REST API is continuing its overhaul with the following additions to the v2 API
-
Cluster Resource (ISPN-10268)
-
Cache Resource (ISPN-9772 ISPN-10392)
-
Counter Resource (ISPN-10151 ISPN-10152)
The REST endpoint now fully supports authorization (ISPN-8736)
Reactive API
The first implementation of our new Reactive API have been merged. This is still work in progress and the API will receive major changes until the Final release. The new API includes a new API module and a new KeyValueStore Hot Rod client where search, continuous search and Key Value store methods are included.
Cross-Site Replication
Async mode cross-site replication received 2 major improvements:
-
async mode is now able to detect disconnections between sites and bring the site offline based on <take-offline> configuration (ISPN-10180)
-
track and exposes the average replication times for asynchronous requests (ISPN-9457)
Non-blocking
-
Non-blocking Hot Rod authentication (ISPN-9841)
-
Non-blocking REST endpoint (ISPN-10210)
-
Update internal remote listener code to support non blocking (ISPN-9716)
-
Update internal embedded listeners to be non blocking (ISPN-9715)
Removal/deprecations
A new major release is also an opportunity to do some house cleaning.
Deprecations
-
Deprecate GridFileSystem and org.infinispan.io stream implementations (ISPN-10298)
-
Deprecated Total Order transaction mode (ISPN-10259)
Removals
-
AtomicMap implementations removed (ISPN-10230)
-
Remove deprecated org.infinispan.io classes (ISPN-10297)
-
Remove org.infinispan.tools.ConfigurationConverter (ISPN-10231)
-
Remove compatibility mode (ISPN-10370)
If you are curious you can read the detailed release notes including all fixed issues. As usual you can ask questions on the forum, StackOverflow and interactively on our Zulip Chat. Please report any bugs you find on our Issue Tracker. Going back to our three-week schedule, our next release will be Beta5, three weeks from now.
Tags: beta release
Friday, 12 July 2019
Infinispan Operator 0.3.0 expands container and security configuration!
Infinispan Operator 0.3.0 is now available with expanded configuration and security options:
Container Configuration
With this release of the Infinispan Operator, you can configure explicit CPU and memory limits for individual containers. The defaults are 0.5 CPUs and 512Mi of memory.
The Operator also lets you pass extra JVM options, which is useful for tracking native memory consumption or extra GC logging parameters.
Security Configuration
Starting with 0.3.0, credentials are automatically generated for data connector and management users when you instantiate the Infinispan Operator.
The default usernames are developer and admin for the data connector user and management user, respectively.
Generated passwords are stored in Kubernetes Secret instances. You can extract the passwords as follows:
For convenience, the default usernames are also stored in the secret. Using the jq command line tool, you can inspect both the username and password values with a single command:
If you want to set custom credentials for the data connector and management users, create Kubernetes Secret instances as follows:
When using a Credentials type authentication, the referenced secrets must contain username and password fields.
Trying It Out!
The easiest way to get started with the Infinispan Operator is via the simple tutorial. The Operator is compatible with vanilla Kubernetes environments, such as Minikube, as well as Red Hat OpenShift.
Available via Operator Hub
Install the Infinispan Operator directly from the Operator Hub, which is available out of the box on all OpenShift 4 versions. If you’re using a vanilla Kubernertes environment, you might need to install the Operator Lifecycle Manager before you can install via the Operator Hub.
The Infinispan Operator is also included in the community for Kubernetes Operators is available from operatorhub.io.
What’s Next?
The Operator configuration does not yet provide all capabilities available for Infinispan servers. We’re working through a process of configuration specification that distills the server configuration into a simple, easy to use, set of configuration options. The current proposal is being discussed openly here.
Infinispan 10 brings a brand new server that’s no longer based on WildFly. The Operator 0.x series will remain focused on Infinispan 9.x server, with Operator 1.x series focusing on Infinispan 10 and onwards.
Cheers, Galder
Tags: release openshift kubernetes operator
Friday, 05 April 2019
Infinispan Spring Boot Starter 2.1.5.Final and 1.0.7.Final are out!
Dear Infinispan and Spring Boot users,
We have just released Infinispan Spring Boot Starter 2.1.5.Final and 1.0.7.Final.
2.1.5.Final
* * 2.1.5.Final is using Infinispan 9.4.11.Final and Spring-Boot 2.1.4.RELEASE.
Important Spring-Boot bug fix
Previous versions of Spring-Boot 2.1.x contained a bug related to the multi-release jars. Infinispan contains multi-release jars, in consequence, we could not run our applications using java -jar with Java 11 (Java 8 worked fine). For additional explanations, read here. Spring-Boot team has fixed this bug and released the correction in Spring-Boot 2.1.4.RELEASE, along with many other features and bug fixes, so consider upgrading soon.
Statistics on Client/Server mode and Actuator
Statistics configuration in client/server mode for the client evolved in the latest Infinispan versions. As a remainder, to activate actuator statistics in client/server mode : "Configure 'infinispan.remote.statistics=true' in the", application.properties or - Configure ''infinispan.client.hotrod.statistics=true" in the hotrod-client.properties or - Configure by code, for example:
@Bean public InfinispanRemoteConfigurer infinispanRemoteConfigurer() \{ return () → new ConfigurationBuilder().statistics().enable().build(); }
===== JMX
If you want to use Infinispan and JMX, for example on Client/Server mode, set the 'jmx' property 'true' as explained above with the 'statistics' property. However, you might get a javax.management.InstanceAlreadyExistsException because both Infinispan and Spring will try to register the MXBean.
The correction will land on the next starter release. If you need to avoid this error today, you can tell Spring-Boot not to register the bean with the following code (Thanks Stéphane Nicoll for the tip!):
Testcontainers
This version includes an integration test using Testcontainers, JUnit5 and the Infinispan Server. Grab a look here if you are curious.
1.0.7.Final
* * 1.0.7.Final upgrades to 1.5.19.RELEASE and Infinispan 9.4.11.Final.
⭐ Don’t forget to star the project in GitHub if you like the starter! ⭐
You can find these releases in the maven central repository.
Please report any issues in our issue tracker and join the conversation in our Zulip Chat to shape up our next release.
Enjoy,
The Infinispan Team
Tags: release spring boot
Friday, 22 February 2019
Infinispan Spring Boot Starter 2.1.4.Final is out!
Dear Infinispan and Spring Boot users,
We have just released Infinispan Spring Boot 2.1.4.Final.
2.1.4.Final is using the last Infinispan Release 9.4.8.Final and Spring-Boot 2.1.3.RELEASE.
You can find this release in the maven central repository.
Please report any issues in our issue tracker and join the conversation in our Zulip Chat to shape up our next release.
Enjoy,
The Infinispan Team
Tags: release spring boot